Introduction of Research
-Structural control of metal materials
| Al alloys |
|---|
General-purpose aluminum alloy (Al-Mg-Si alloy) From aluminum sashes and doors to car bodies 
|
Highest strength aluminum alloy (Al-Zn-Mg alloy) Expanded from baseball bats to hydrogen storage containers. 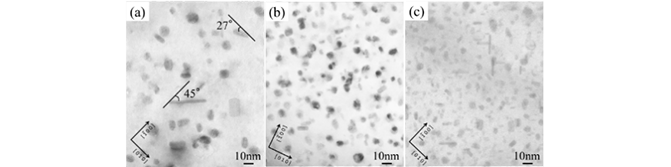
|
| Mg alloys |
|
Material for practical use (the basic characteristics are still unknown) 
Characteristic: It is the lightest of all practical alloys and can be applied with the same heat treatment method as aluminum alloys. On the other hand, it has poor heat resistance and corrosion resistance. |
| Cu alloys |
General-purpose copper alloy (Cu-Zn alloy: brass) Characteristic: It is nourished in various shapes because it is easy to process. 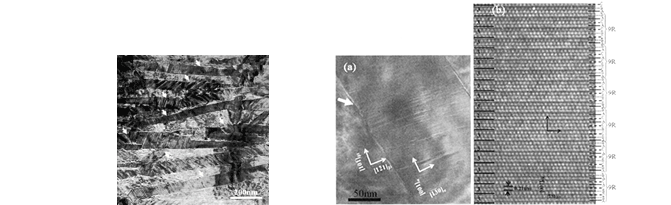
|
Corson alloy (Cu-Ni-Si alloy) Characteristics: By adding general-purpose nickel and silicon, the strength can be easily increased. 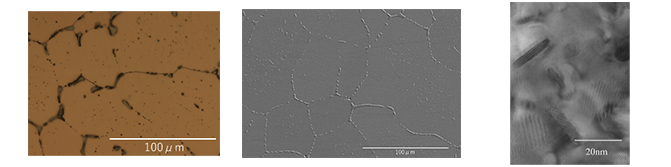
|
| Superconducting material |
Metal-based material (Ni3Sn) Characteristics: It is stable as a superconducting material and is a general-purpose practical material. 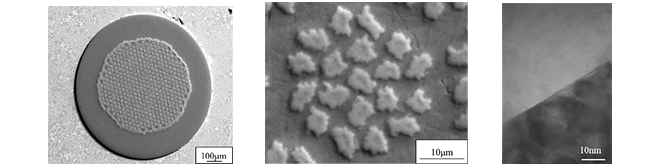
|
Development of new materials through research and development
| Multifunctional composite materials |
|---|
Materials with new functions by combining metals and ceramics Characteristics: A material that combines the ductility of aluminum with the synthesis of ceramics, and also shares the light emitting properties, magnetism, superconducting properties, and photocatalytic properties. 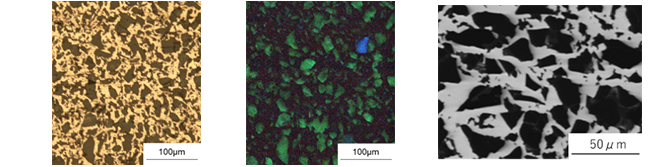
|
Functional thin film Characteristics: It becomes an excellent tool by attaching a ceramic thin film to the surface of steel. 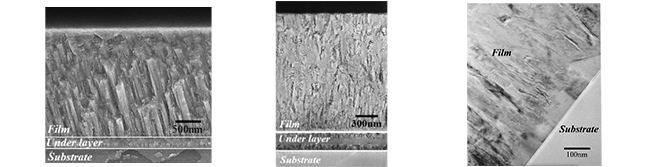
|


